Publications
The first paper release from MAPS is presented in a special issue of the Astrophysical Journal Supplement. See below for summaries of the individual papers, links to the manuscripts, and where to download the relevant data products.
MAPS I. Program Overview and Highlights
- Karin I. Öberg, Viviana V. Guzmán, Catherine Walsh, Yuri Aikawa, Edwin A. Bergin, Charles J. Law, Ryan A. Loomis, Felipe Alarcón, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Jennifer B. Bergner, Yann Boehler, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Kenji Furuya, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Nicolas T. Kurtovic, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Laura M. Pérez, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Anibal Sierra, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Abygail R. Waggoner, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
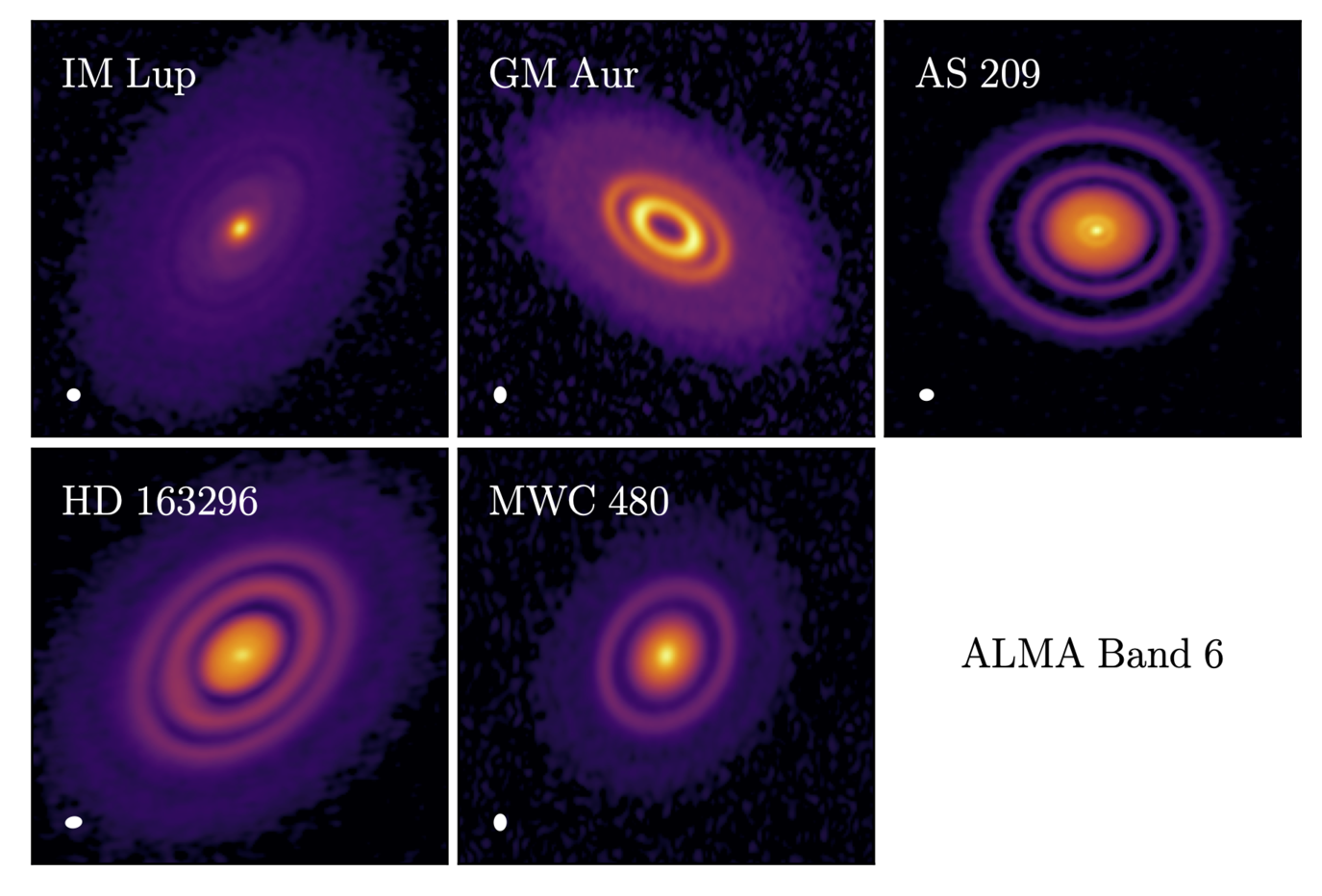
The MAPS project set out to map the distribution of molecules in planet-forming disks at unprecedented detail. The results show an astonishing diversity in abundances and distributions of key chemicals across planet-forming disks, including a wealth of chemical substructures. The inferred range of chemical environment within which planets assemble implies that planetary chemical compositions, including access to water and organics, may vary substantially between one planetary system and another.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS II. CLEAN Strategies for Synthesizing Images of Molecular Line Emission in Protoplanetary Disks
- Ian Czekala, Ryan A. Loomis, Richard Teague, Alice S. Booth, Jane Huang, Gianni Cataldi, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Catherine Walsh, Arthur D. Bosman, Viviana V. Guzmán, Romane Le Gal, Karin I. Öberg, Yoshihide Yamato, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Laura M. Pérez, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Takashi Tsukagoshi, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
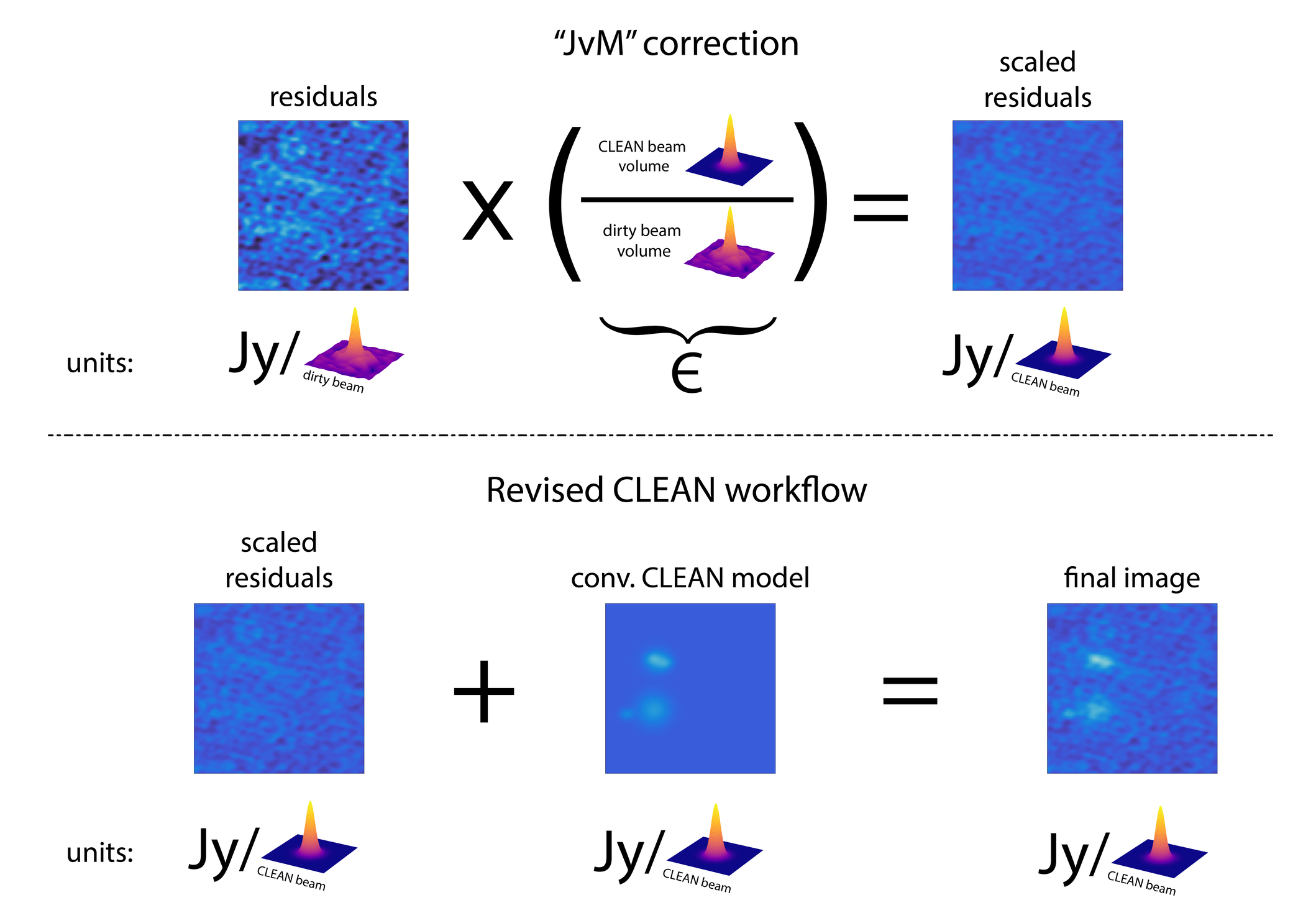
MAPS II describes our multi-stage workflow (built around the CASA tclean image deconvolution procedure) that we used to generate the core data product of the MAPS LP: the position-position-velocity image cubes for each spectral line. We describe how to produce image cubes with accurate fluxes via the “JvM” correction, a procedure that is generally applicable to any image synthesized via CLEAN deconvolution but is especially critical for faint emission (and is not part of the default CASA imaging workflow). We also explain how we used visibility tapering to promote a common, fiducial beam size and contextualize the interpretation of signal to noise ratio when detecting molecular emission from protoplanetary disks.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS III. Characteristics of Radial Chemical Substructures
- Charles J. Law, Ryan A. Loomis, Richard Teague, Karin I. Öberg, Ian Czekala, Sean M. Andrews, Jane Huang, Yuri Aikawa, Felipe Alarcón, Jaehan Bae, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, Yann Boehler, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Kenji Furuya, Viviana V. Guzmán, John D. Ilee, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Anibal Sierra, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
MAPS III presents a systematic analysis of chemical substructures in 18 molecular lines toward the five MAPS disks. We identify more than 200 chemical substructures with a wide diversity of radial morphologies — including rings, gaps, and plateaus — which suggests that planets form in varied chemical environments across disks and even at different radii within the same disk. Interior to 150 au, the majority of line emission substructures are spatially coincident with substructures in the millimeter continuum, while at larger radii, most cannot be directly linked to dust substructure. Overall, this indicates physical and chemical links between midplanes and warm, elevated molecular emission layers in the inner planet-forming zones of disks and highlights the powerful potential of chemical substructures as probes of disk characteristics, in addition to influencing the environments within which planets assemble.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS IV. Emission Surfaces and Vertical Distribution of Molecules
- Charles J. Law, Richard Teague, Ryan A. Loomis, Jaehan Bae, Karin I. Öberg, Ian Czekala, Sean M. Andrews, Yuri Aikawa, Felipe Alarcón, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Kenji Furuya, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Laura M. Pérez, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Daniela Soto, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
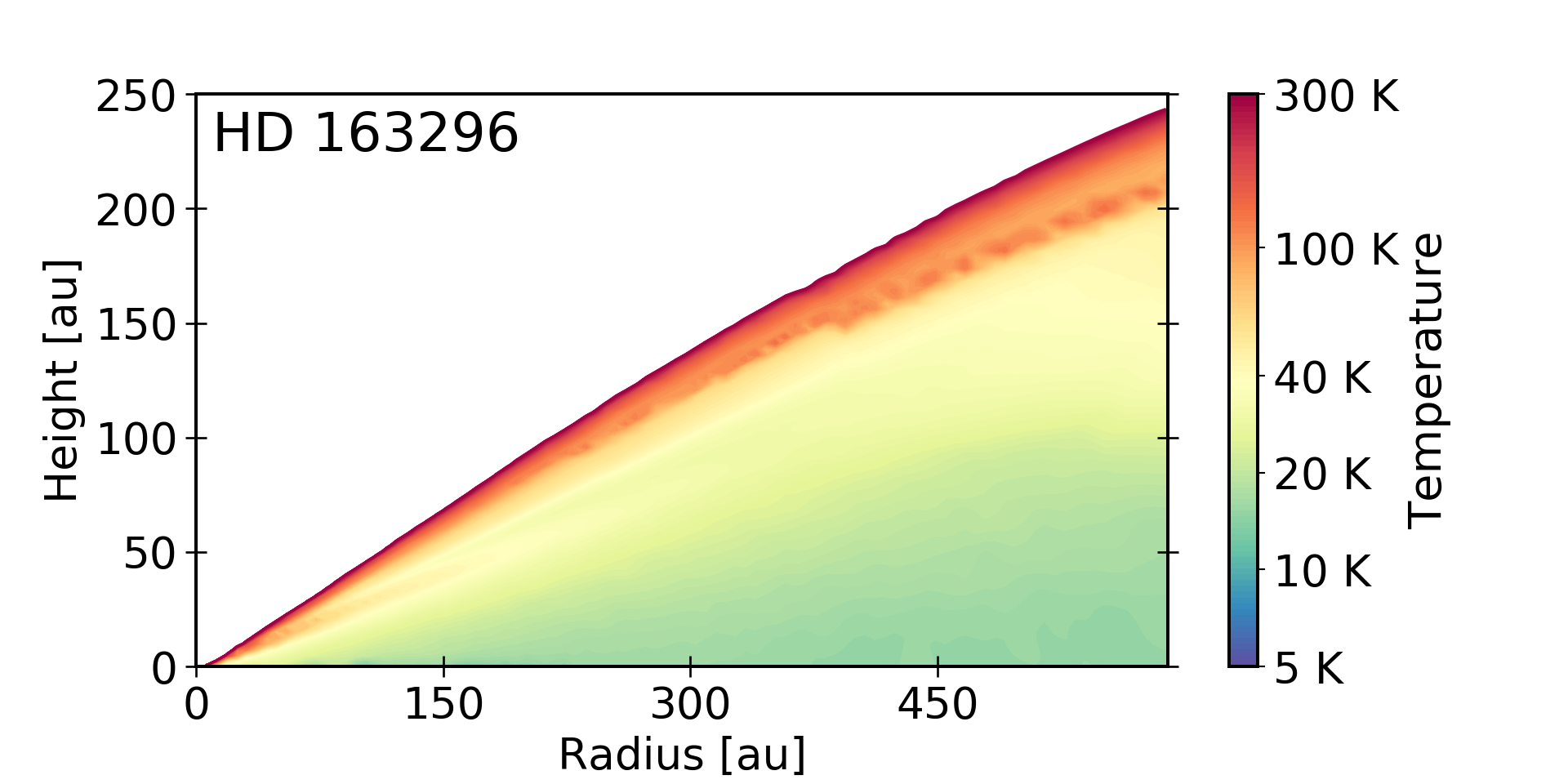
MAPS IV measures the line emission surfaces of a suite of CO isotopologues and when possible, for C2H and HCN. There is considerable variation in the inferred emitting heights among the MAPS disks, but we find that 12CO emission consistently traces the most elevated regions, while emission from the less abundant 13CO and C18O probes deeper toward the disk midplanes. We use these surfaces to trace 2D temperature structures for each disk and identify dips in both temperature or vertical height, some of which are associated with gaps and rings in line or continuum emission. These substructures may be due to local changes in CO column density, gas surface density, or gas temperatures but further thermo-chemical modeling is required to constrain their origins and ultimately to relate the chemical compositions of elevated disk layers with those of planet-forming material in disk midplanes.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS V. CO Gas Distributions
- Ke Zhang, Alice S. Booth, Charles J. Law, Arthur D. Bosman, Kamber R. Schwarz, Edwin A. Bergin, Karin I. Öberg, Sean M. Andrews, Viviana V. Guzmán, Catherine Walsh, Chunhua Qi, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Feng Long, David J. Wilner, Jane Huang, Ian Czekala, John D. Ilee, Gianni Cataldi, Jennifer B. Bergner, Yuri Aikawa, Richard Teague, Jaehan Bae, Ryan A. Loomis, Jenny K. Calahan, Felipe Alarcón, François Ménard, Romane Le Gal, Anibal Sierra, Yoshihide Yamato, Hideko Nomura, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Laura M. Pérez, Leon Trapman, Yao Liu, Kenji Furuya
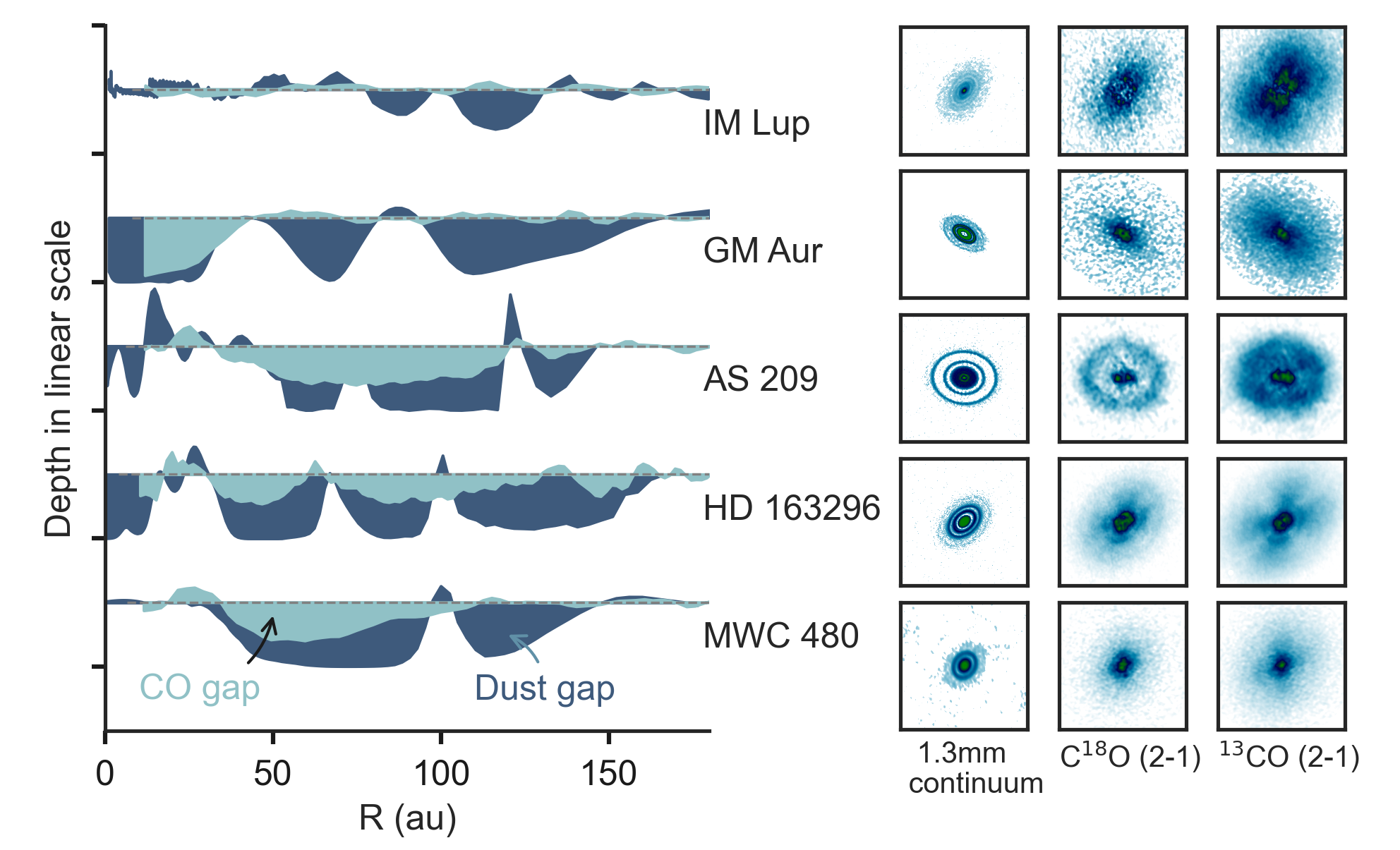
Using observations of five CO isotopologue lines, we find that the CO-to-H2 ratios in the warm molecular layers of the five MAPS disks are much lower than the canonical ISM ratio. The CO column density distributions vary significantly among five disks. Most CO gaps coincide with dust gaps, but CO gaps are much shallower than those seen in dust gaps. The spatial coincidence and depth difference are expected if these gaps are opened by planets.
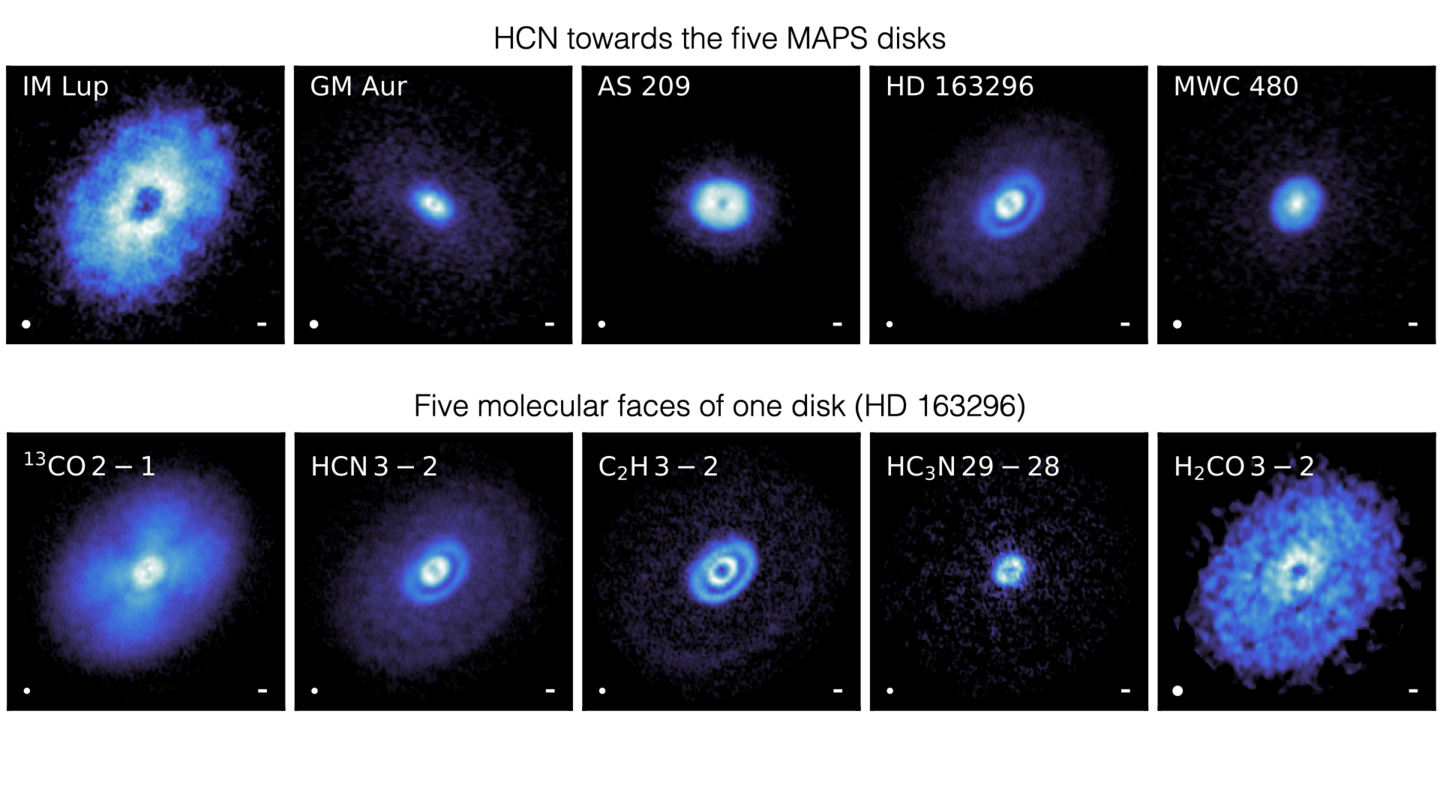
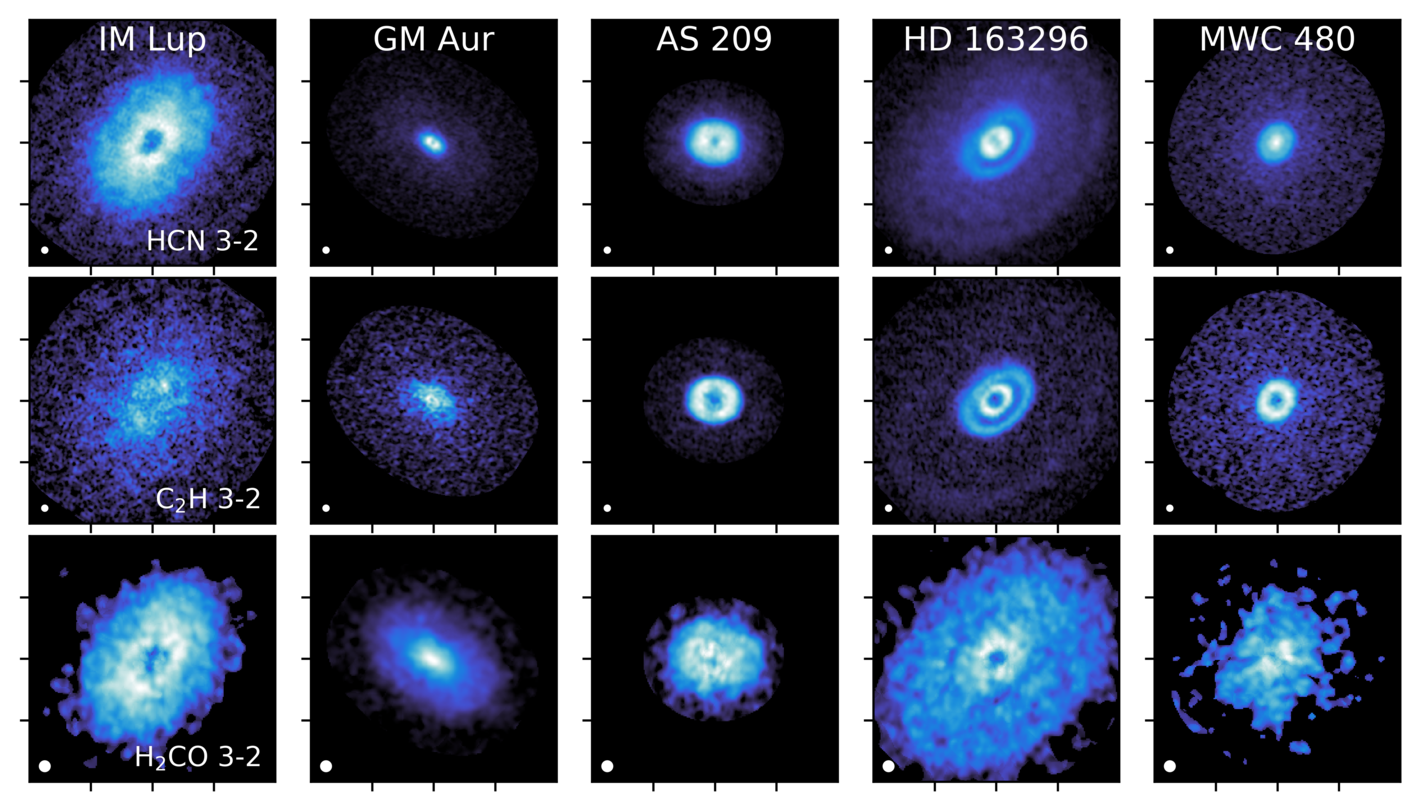
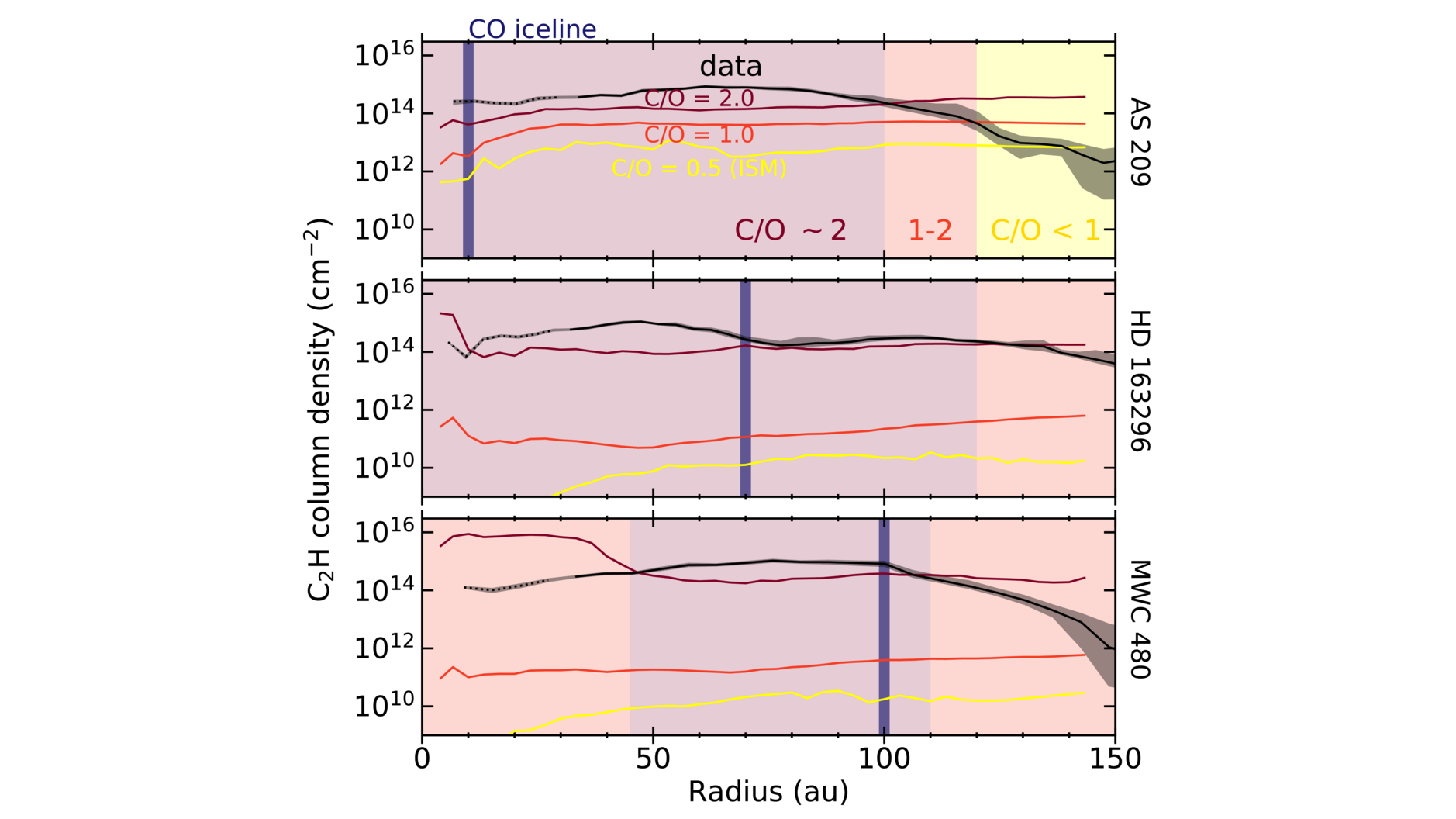
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS VI. Distribution of the Small Organics HCN, C2H, and H2CO
- Viviana V. Guzmán, Jennifer B. Bergner, Charles J. Law, Karin I. Öberg, Catherine Walsh, Gianni Cataldi, Yuri Aikawa, Edwin A. Bergin, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, Sean M. Andrews, Ryan A. Loomis, Ke Zhang, Romane Le Gal, Felipe Alarcón, John D. Ilee, Richard Teague, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, David J. Wilner, Feng Long, Kamber R. Schwarz, Arthur D. Bosman, Laura M. Pérez, François Ménard, Yao Liu
HCN, C2H, and H2CO are small molecules that are bright in disks, and give us access to the organic material that could eventually be incorporated into planets. Our results show that the inner 50 au of these disks is rich in organic material, suggesting that planets forming in these disks have the basic ingredients to form the building blocks of life.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS VII. Substellar O/H and C/H and Superstellar C/O in Planet-feeding Gas
- Arthur D. Bosman, Felipe Alarcón, Edwin A. Bergin, Ke Zhang, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Karin I. Öberg, Viviana V. Guzmán, Catherine Walsh, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Jennifer B. Bergner, Alice S. Booth, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Kenji Furuya, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, David J. Wilner
We investigated the composition of gas around the locations that giant planets are expected to be forming. We find that the gas that feeds these forming gas giants is very distinct from the composition of the star, more carbon relative to oxygen and low amounts of both carbon and oxygen relative to hydrogen. This should lead to giant planets that have very distinctive compositions.
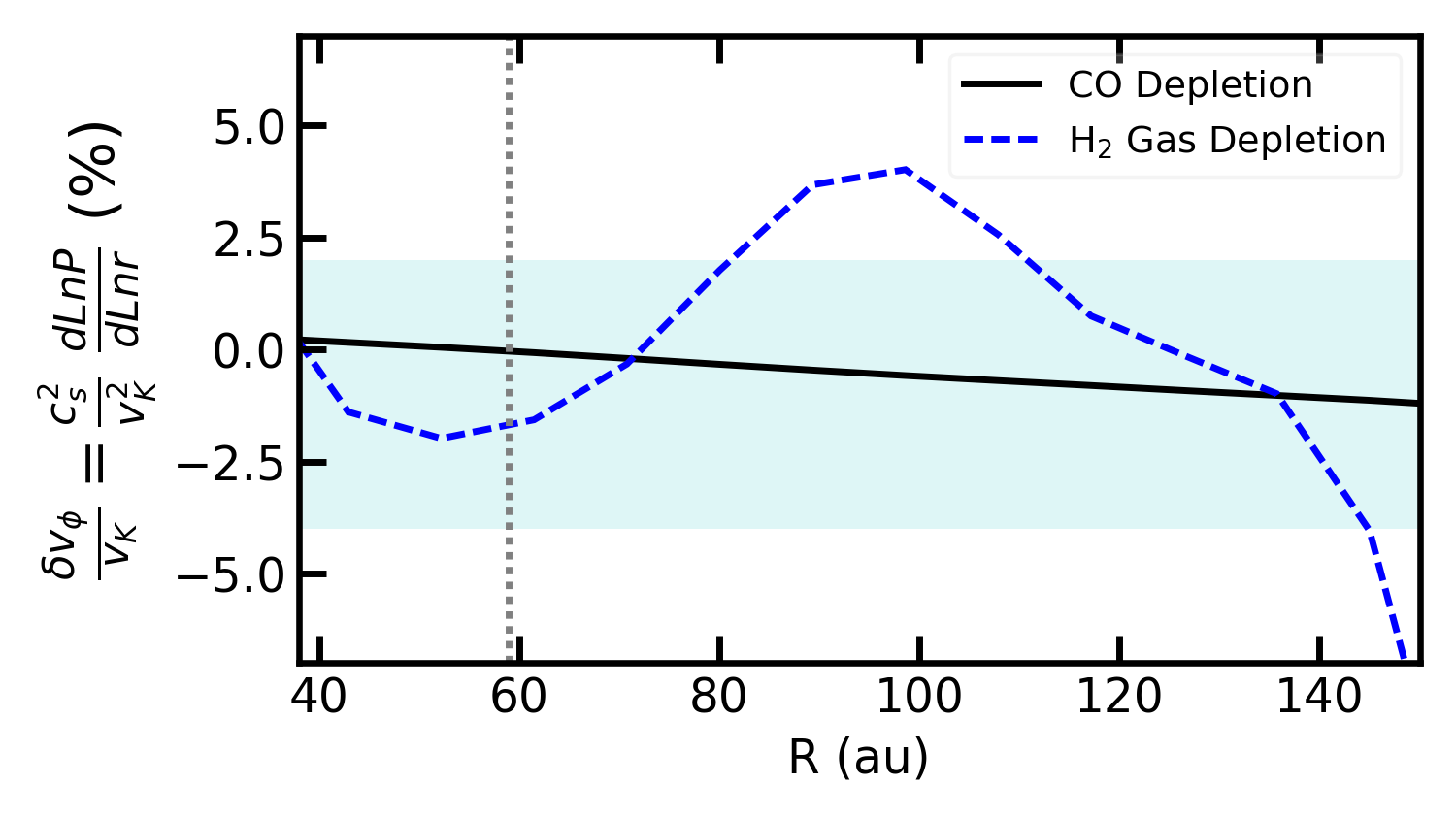
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS VIII. CO Gap in AS 209—Gas Depletion or Chemical Processing?
- Felipe Alarcón, Arthur D. Bosman, Edwin A. Bergin, Ke Zhang, Richard Teague, Jaehan Bae, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Alice S. Booth, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, François Ménard, Karin I. Öberg, Kamber R. Schwarz, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner
Line and dust emission substructures in AS 209 show differences in the disk distribution of volatiles with respect to dust gaps. We determine the origin of the C18O emission substructure, showing that CO chemical processing is dominant over gas depletion due to a giant planet.
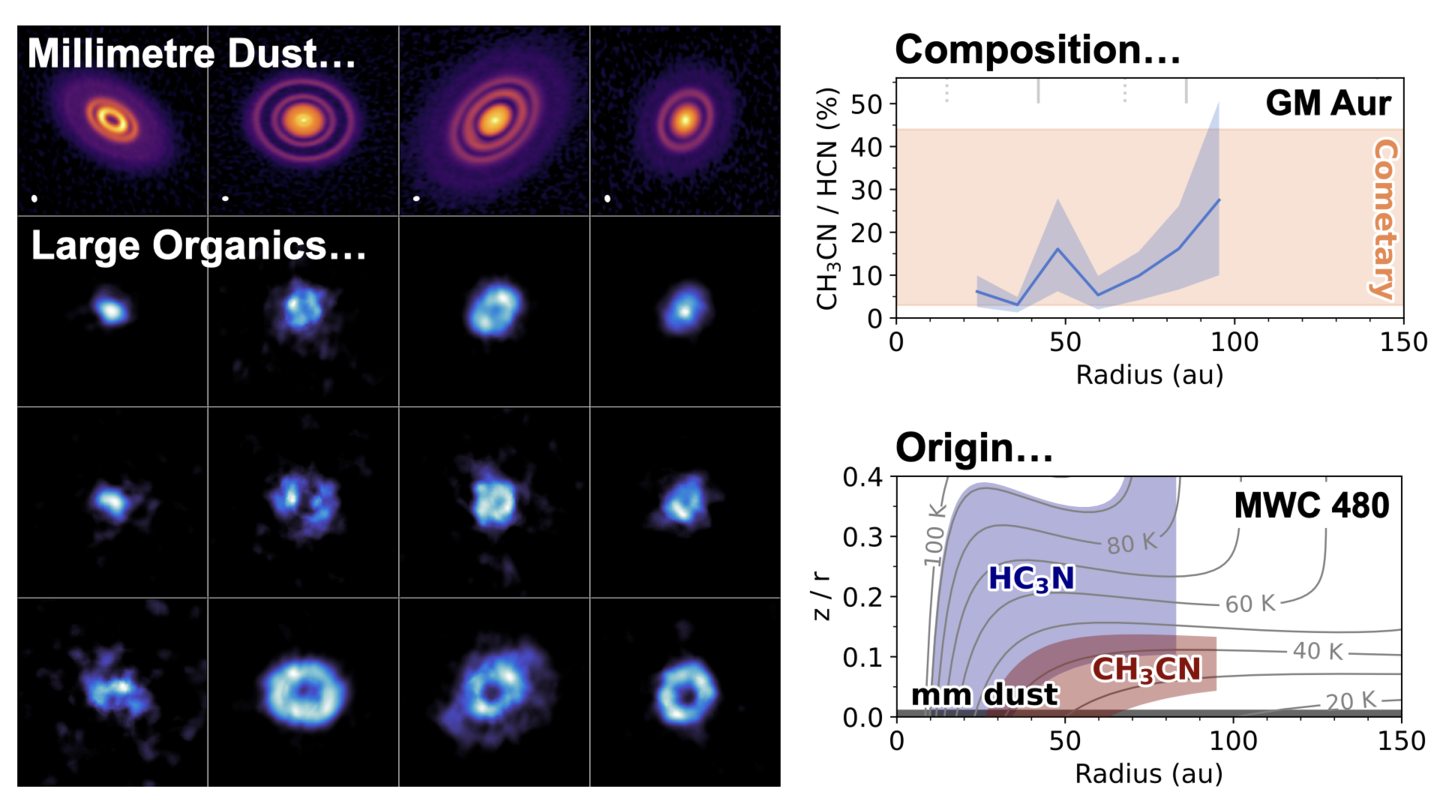
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS IX. Distribution and Properties of the Large Organic Molecules HC3N, CH3CN, and c-C3H2
- John D. Ilee, Catherine Walsh, Alice S. Booth, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, Arthur D. Bosman, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Karin I. Öberg, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang
MAPS IX investigates the prebiotically-interesting large organic molecules HC3N, CH3CN, c-C3H2, which are robustly detected in all disks apart from IM Lup. We use rotation diagram analysis to infer a radially-resolved column density and rotational temperature profile for each molecule in each disk. Based on this, we find significant reservoirs of these large organics in the inner 50-100 au of the disks, emitting from very close to the midplane. Comparison of the ratio of small to large organic molecules in the disks suggests a similar composition to observations of comets. In combination, our results suggest that planets form in an environment rich with precursors of life-essential molecules, and this material has a composition similar to our own Solar System.
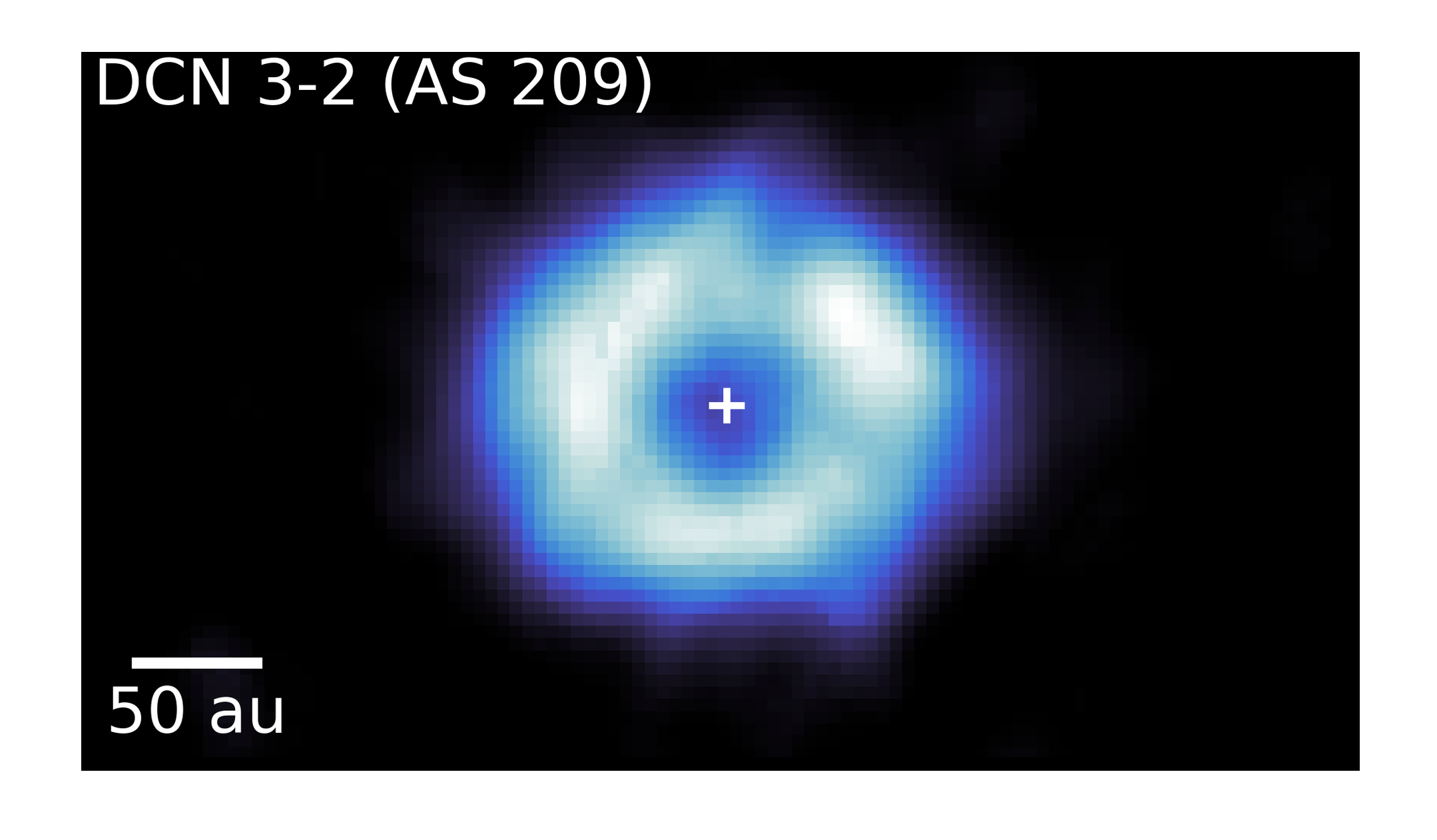
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS X. Studying Deuteration at High Angular Resolution toward Protoplanetary Disks
- Gianni Cataldi, Yoshihide Yamato, Yuri Aikawa, Jennifer B. Bergner, Kenji Furuya, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, Ryan A. Loomis, Chunhua Qi, Sean M. Andrews, Edwin A. Bergin, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Karin I. Öberg, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
We studied the deuterated molecules DCN and N2D+. These are the deuterated versions of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and diazenylium (N2H+), with the hydrogen atom (H) replaced by a deuterium atom (D, also known as heavy hydrogen). Our observations informed us about the chemical processes that produce deuterated molecules in a protoplanetary disk. Comparing to the amount of deuterated molecules in comets or asteroids can help us to understand the formation history of the Solar System.
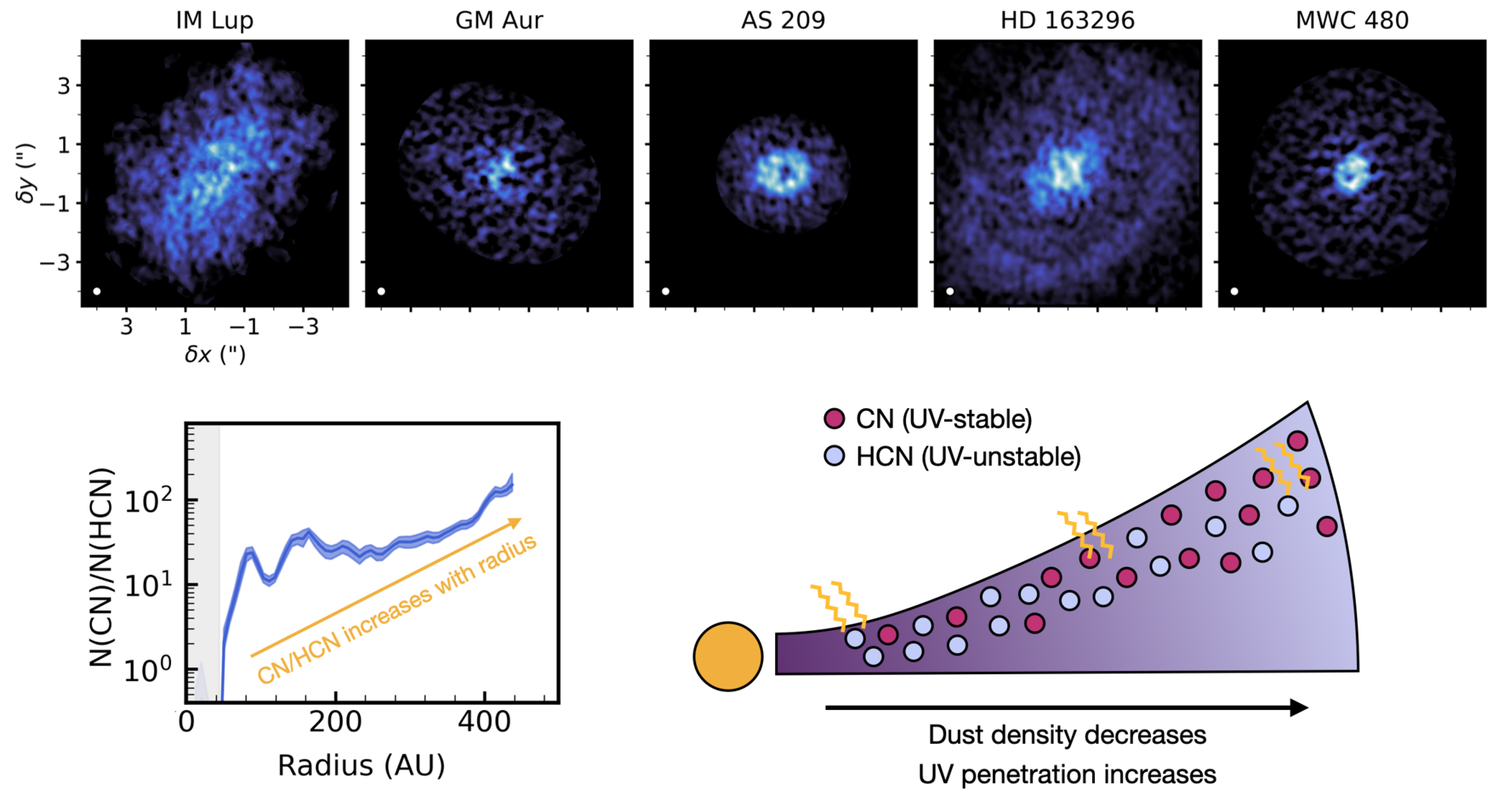
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XI. CN and HCN as Tracers of Photochemistry in Disks
- Jennifer B. Bergner, Karin I. Öberg, Viviana V. Guzmán, Charles J. Law, Ryan A. Loomis, Gianni Cataldi, Arthur D. Bosman, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Edwin A. Bergin, Alice S. Booth, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Romane Le Gal, Feng Long, Hideko Nomura, François Ménard, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato
UV radiation is thought to play a key role in driving the formation of new molecules in planet-forming disks. Using the molecular tracer CN, we see evidence for a very active photochemistry within the MAPS disks, with particularly strong UV penetration in the outer disk and possibly in several dust gaps. These regions may be especially favorable for forming new molecules in disks. We also find that the compositions of different elevations of the disk seem to be connected, implying that chemistry in the disk surface may be linked to the chemistry in the planet-forming midplane.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XII. Inferring the C/O and S/H Ratios in Protoplanetary Disks with Sulfur Molecules
- Romane Le Gal, Karin I. Öberg, Richard Teague, Ryan A. Loomis, Charles J. Law, Catherine Walsh, Edwin A. Bergin, François Ménard, David J. Wilner, Sean M. Andrews, Alice S. Booth, Yuri Aikawa, Gianni Cataldi, Jennifer B. Bergner, Arthur D. Bosman, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Kenji Furuya, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Hideko Nomura, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang
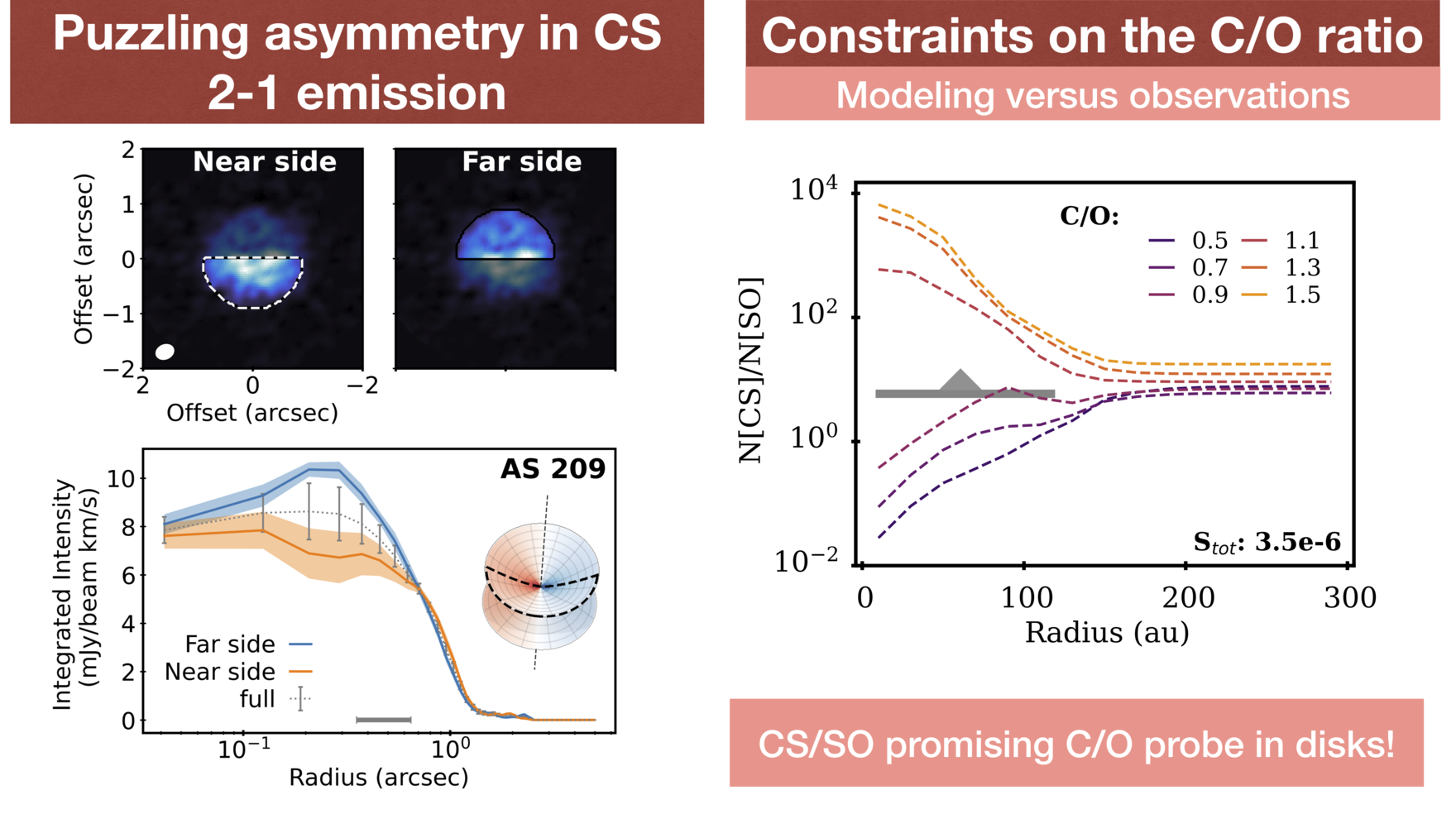
MAPS XII investigates sulfur-bearing molecules in the MAPS target disks, including CS, C2S and SO. For MWC 480, complementary observations allow us to derive a column density ratio of H2CS/CS ~ 2-3, suggesting that a substaintial fraction of the sulphur reservoir is in organic form (e.g., CxHySz). Using astrochemical models, we demonstrate that N(CS)/N(SO) is a promising probe of the elemental C/O ratio. We also find an S/H ratio between the solar and dense molecular core values, suggesting some of the sulfur reservoir is unlocked at the protoplanetary disk stage.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XIII. HCO+ and Disk Ionization Structure
- Yuri Aikawa, Gianni Cataldi, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang, Alice S. Booth, Kenji Furuya, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, Arthur D. Bosman, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Viviana V. Guzman, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Karin I. Öberg, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner
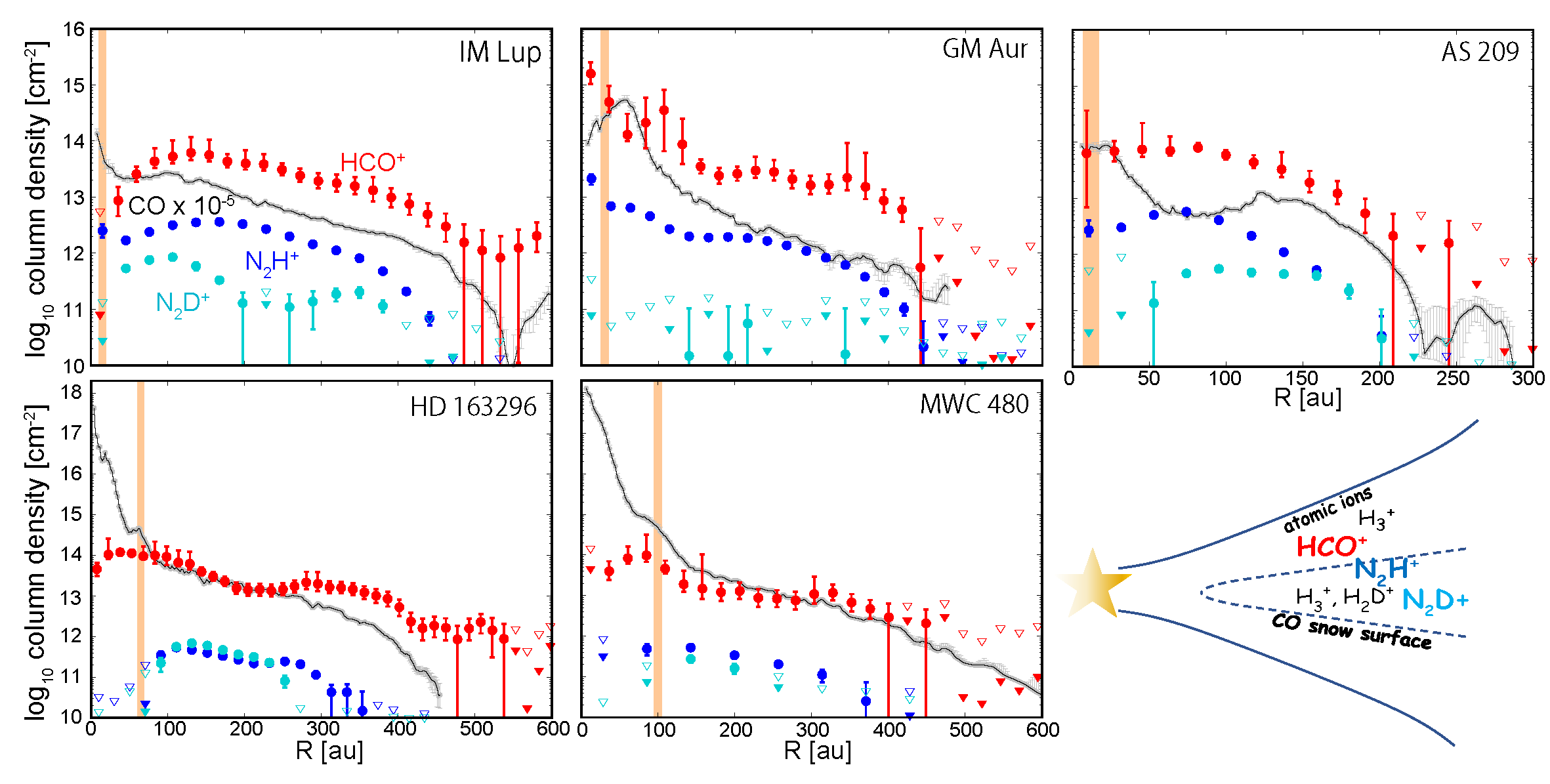
We investigated the ionization degree in protoplanetary disks by observing the major ion molecules. HCO+ shows the enhanced ionization at some pronounced disk gaps, while N2H+ and N2D+ suggest ionization rate near the midplane vary among disks.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XIV. Revealing Disk Substructures in Multiwavelength Continuum Emission
- Anibal Sierra, Laura M. Pérez, Viviana V. Guzmán, Ke Zhang, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Catherine Walsh, Charles J. Law, Chunhua Qi, David J. Wilner, Feng Long, François Ménard, Gianni Cataldi, Ian Czekala, Jaehan Bae, Jane Huang, Jennifer B. Bergner, John D. Ilee, Karin I. Öberg, Myriam Benisty, Richard Teague, Romane Le Gal, Ryan A. Loomis, Sean M. Andrews, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yao Liu, Yoshihide Yamato, Yuri Aikawa
The morphology of the emission from dust grains in protoplanetary disk depends on the wavelength at which they are observed. Differences in their appearance help us infer what is the size of the dust grains and their mass distribution at different locations of the disk, particularly in the rings and gaps observed.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XV. Tracing Protoplanetary Disk Structure within 20 au
- Arthur D. Bosman, Edwin A. Bergin, Ryan A. Loomis, Sean M. Andrews, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Richard Teague, Karin I. Öberg, Viviana V. Guzmán, Catherine Walsh, Yuri Aikawa, Felipe Alarcón, Jaehan Bae, Jennifer B. Bergner, Alice S. Booth, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Laura M. Pérez, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Anibal Sierra, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Yoshihide Yamato, David J. Wilner, Ke Zhang
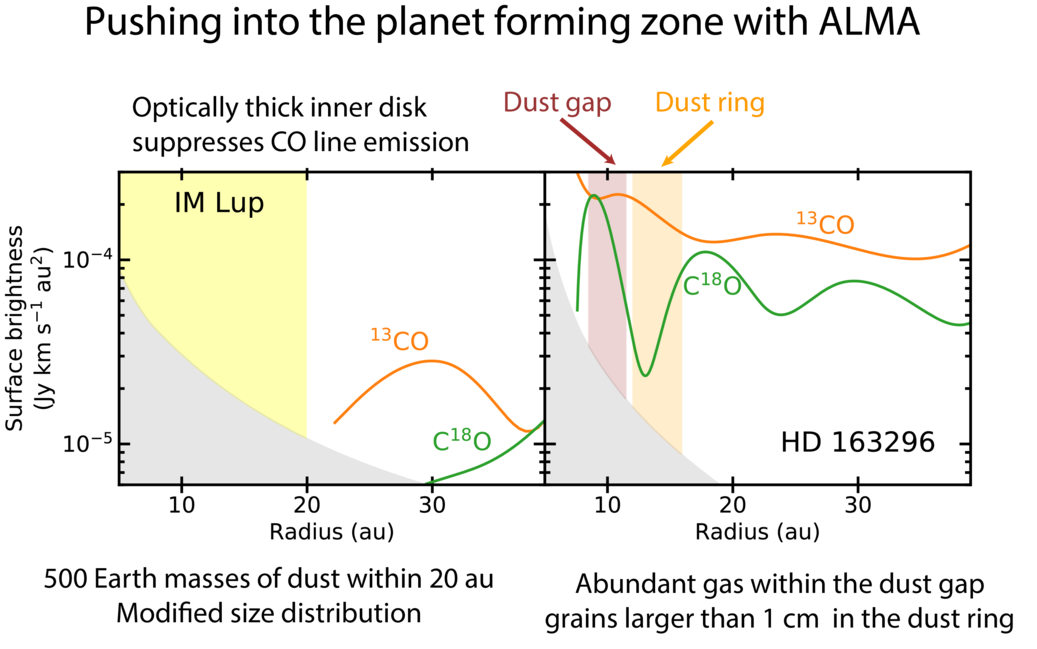
We use the Keplerian rotation pattern of proto-planetary disks to look for structure hidden within the central resolution element in the MAPS data. We find structures in the inner planet-forming zones of these disks that went unresolved in the MAPS images. From these structures we infer that IM Lup is on the verge of efficient giant planet formation and that grains are efficiently grown in dust traps in the inner 15 au of AS 209 and HD 163296.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XVI. Characterizing the Impact of the Molecular Wind on the Evolution of the HD 163296 System
- Alice S. Booth, Benoît Tabone, John D. Ilee, Catherine Walsh, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Jennifer B. Bergner, Arthur D. Bosman, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Karin I. Öberg, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Richard Teague, Takashi Tsukagoshi, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang
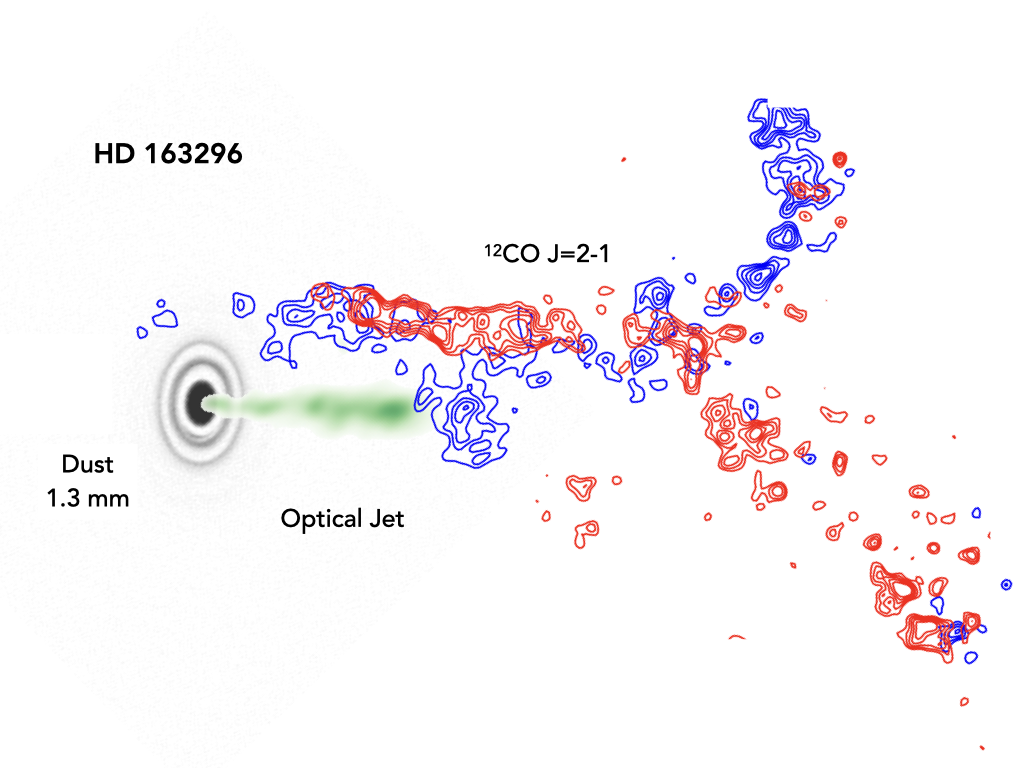
MAPS XVI focuses on characterising the molecular wind that is launched from the inner HD 163296 disk traced by carbon monoxide gas. We find that the angular momentum extracted from the system by the wind is sufficient to drive accretion in the inner disk thus giving key insight into the physics governing the formation and evolution of planets in this system.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XVII. Determining the 2D Thermal Structure of the HD 163296 Disk
- Jenny K. Calahan, Edwin A. Bergin, Ke Zhang, Kamber R. Schwarz, Karin I. Öberg, Viviana V. Guzmán, Catherine Walsh, Yuri Aikawa, Felipe Alarcón, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Jennifer B. Bergner, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Gianni Cataldi, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Chunhua Qi, Richard Teague, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato
In MAPS XVII we determine the gas temperature within the massive, planet-forming disk HD 163296 using the high resolution MAPS observations of CO isotopologues. With a detailed model fit to all relevant data we reveal the thermal structure of disk writ large, constrain the planet-forming mass reservior, and show that the gaps associated with potential planets are modestly warmer than their surroundings.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XVIII. Kinematic Substructures in the Disks of HD 163296 and MWC 480
- Richard Teague, Jaehan Bae, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Edwin A. Bergin, Jennifer B. Bergner, Yann Boehler, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Gianni Cataldi, Ian Czekala, Viviana V. Guzmán, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Karin I. Öberg, Laura M. Pérez, Kamber R. Schwarz, Anibal Sierra, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang
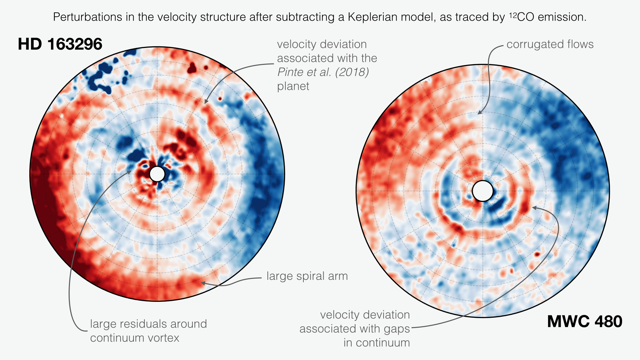
An investigation of the dynamical structure of the protoplanetary disks around HD 163296 and MWC 480 using CO isotopologue line emission. HD 163296 is found to have large, extended velocity perturbations associated with previously inferred embedded planets, characterized by tightly wound spiral structures. MWC 480 displays a comparable level of velocity substructure, but in a more azimuthally symmetric morphology with several rings of vertical flows. MWC 480 is also found to have subtle spiral variations in the gas temperature, indicative of spiral waves driven by an unseen embedded planet.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XIX. Spiral Arms, a Tail, and Diffuse Structures Traced by CO around the GM Aur Disk
- Jane Huang, Edwin A. Bergin, Karin I. Öberg, Sean M. Andrews, Richard Teague, Charles J. Law, Paul Kalas, Yuri Aikawa, Jaehan Bae, Jennifer B. Bergner, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Jenny K. Calahan, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, John D. Ilee, Romane Le Gal, Viviana V. Guzmán, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, François Ménard, Hideko Nomura, Chunhua Qi, Kamber R. Schwarz, Takashi Tsukagoshi, Merel L. R. van't Hoff, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner, Yoshihide Yamato, Ke Zhang
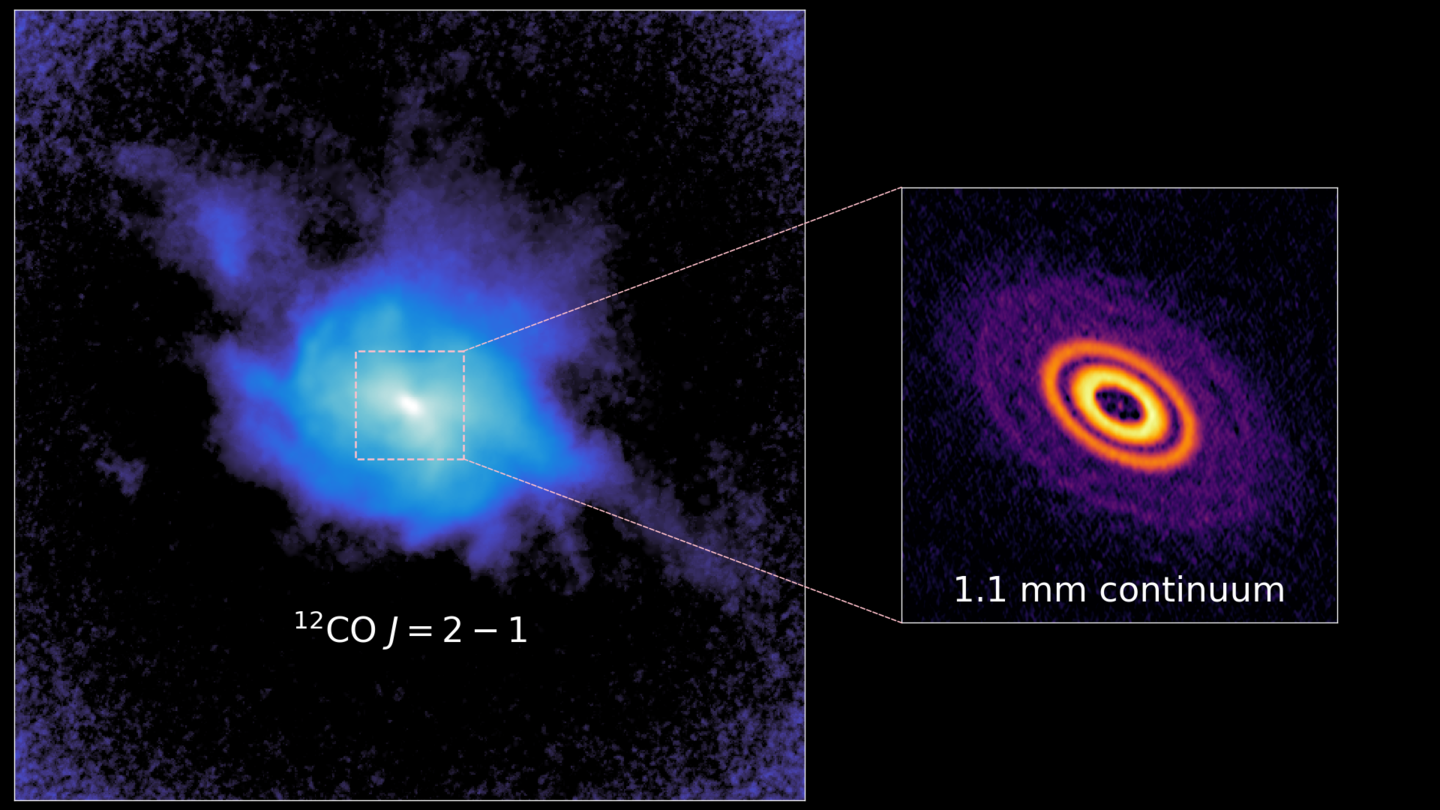
12CO observations reveal non-Keplerian spiral arms, a tail, and diffuse structures at the outer edge of the GM Aur disk. The gas distribution stands in stark contrast to the comparatively compact, axisymmetric millimeter continuum emission tracing large dust grains in the disk. Together, these observations suggest that the disk undergoes complex interactions with its surroundings while planet formation is ongoing.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download DataMAPS XX. The Massive Disk around GM Aurigae
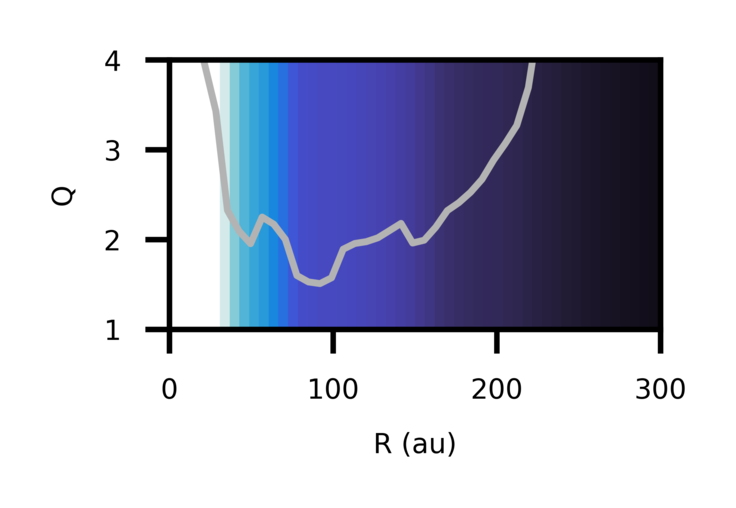
- Kamber R. Schwarz, Jenny K. Calahan, Ke Zhang, Felipe Alarcón, Yuri Aikawa, Sean M. Andrews, Jaehan Bae, Edwin A. Bergin, Alice S. Booth, Arthur D. Bosman, Gianni Cataldi, L. Ilsedore Cleeves, Ian Czekala, Jane Huang, John D. Ilee, Charles J. Law, Romane Le Gal, Yao Liu, Feng Long, Ryan A. Loomis, Enrique Macías, Melissa McClure, François Ménard, Karin I. Öberg, Richard Teague, Ewine van Dishoeck, Catherine Walsh, David J. Wilner
Gas mass remains one of the most difficult protoplanetary disk properties to constrain. We use observations of 11 transitions of the molecule CO from ALMA (probing temperature) and the molecule HD from Herschel (probing mass) to construct a 2D model of the mass and temperature distribution in the GM Aurigae protoplanetary disk. We find that the disk has a low abundance of gas phase CO but a high total disk mass and may be unstable against gravitational collapse in the region around 85 au.
Arxiv PDF SAO/NASA ADS Bibtex Download Data